Green Terms Defined: Energy Recovery Ventilator (ERV)
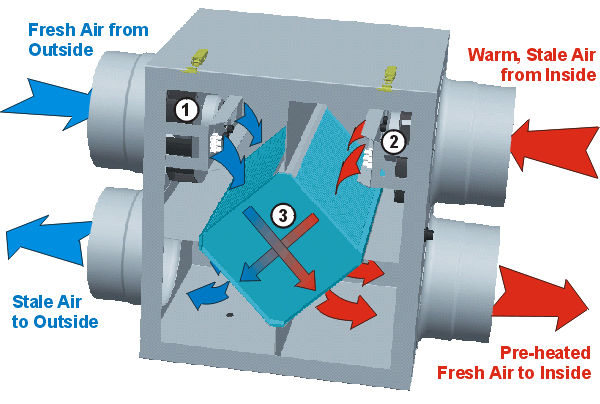
An ERV or Energy Recovery Ventilator is part of a balanced ventilation system that transfers water vapor and heat from one airstream to another. In a mixed humid climate, it works differently in the hot season and the cold season. In hot months, the ERV works to maintain the interior relative humidity of a structure as outside air is conditioned by the ERV entering the fresh air ventilation system. In cold months water vapor is captured from the outgoing air to humidify the incoming air.
An ERV or HRV (heat recovery ventilator) provides fresh air and improved climate control while reducing the energy requirement for heating and cooling a building.